How to Transform MSF Meterpreter to be as Stable as CS Beacon
Preface
Metasploit-Framework and Cobalt Strike are the two most popular penetration platforms in current red team simulations. Metasploit-Framework uses Meterpreter as its post-penetration tool, and Cobalt Strike's corresponding tool is Beacon.
From the perspective of user word-of-mouth and actual usage, Cobalt Strike's Beacon is more favored by domestic users. In addition to the factor that Cobalt Strike provides a friendly graphical interface, most users believe that Beacon is more stable than Meterpreter and permissions are not easily lost.
Where are the differences between Meterpreter and Becaon?
Here we compare windows/beacon_http/reverse_https (Cobalt Strike) and windows/meterpreter/reverse_https (Metasploit-Framework), which are the most commonly used in actual combat.
Core library loading
Both support stager and stagerless methods to load payloads, and the implementation methods are basically the same.
- The loading order of Meterpreter: stager --> metsrv.dll --> stdapi.dll
- The loading order of Becaon: stager --> beacon.dll
It can be seen that when performing basic commands, Meterpreter needs to load an additional stdapi.dll file.
C2 implementation method
Here, C2 refers to Meterpreter's Hander and Beacon's Listener.
- The implementation of Meterpreter's handler: a simple http service implemented by TCPServer combined with resources
- The implementation of Beacon's Listener: implemented based on NanoHTTPD.
Compared with the mature NanoHTTPD, the self-implemented http service may have certain disadvantages in stability.
Communication protocol
Both use https for data communication, but there are differences in the specific transmission methods.
- Meterpreter uses Http1.1 and the keep-alive function is enabled by default and cannot be closed.
- Beacon uses Http1.1 and the keep-alive function is not enabled by default.
Specifically, in the actual usage process, Meterpreter always maintains a TCP connection with the C2 server and does not monitor the status of the TCP connection.
Correspondingly, Beacon establishes a connection with the C2 when requesting tasks/returning results, while there is no network connection with the C2 during the sleep stage.
How to Transform Meterpreter
Optimization of core library loading
The transformation of core library loading is the simplest, or it can't be called a transformation. Metasploit-framework itself supports not automatically loading stdapi.dll. As long as the AutoLoadStdapi parameter is set to False when generating the Handler, it can be done.
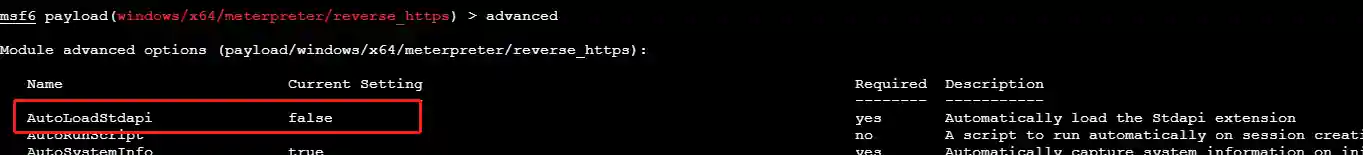
At this time, if there is a payload connecting to this listener, the effect is as follows:
The specific manifestation is that this Session is very similar to a fake session. We need to enter meterpreter and then execute load stdapi to manually load the core library.
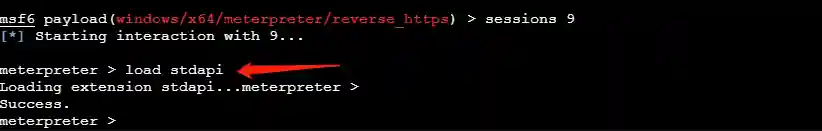
At this time, this Session can be used normally.
Optimization of C2 implementation method
Meterpreter self-implements a simple http service. The author believes that there are the following considerations:
- Achieve the unity of reverse type handler code
- More flexible start/close of services
- Better integration with the Rex::Socket library (Rex::Socket implements the core function of internal network routing)
So what we can do is to fix the problems (Bug) that occur in the http service in various scenarios.
For example:
If you establish a reverse_https handler on the VPS and the port is 443, a common port, you will find that many scanners will scan your handler, resulting in a lot of invalid network connections. If you happen not to set the LURI, there will also be a lot of fake Sessions.
The specific reason is in the following code:
https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework/blob/master/lib/rex/proto/http/server.rb#L372
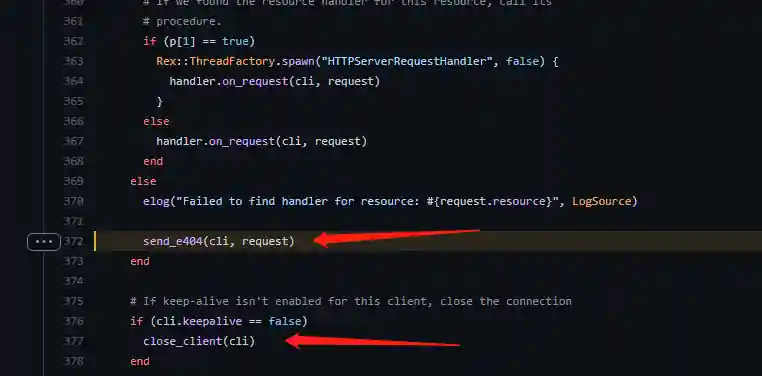
It can be seen that for illegal requests, although MSF will return a 404 page (line 372), if the other party sets the keep-alive header, MSF will not actively close the TCP connection, resulting in a lot of invalid network connections on the port, which will affect the real payload connection.
And the code to solve this Bug is as follows:
That is, the default is to close the connection for illegal requests.
Communication protocol transformation
I think this is the biggest difference between the two, and it is also the direct reason for the instability of meterpreter.
We hope that the logic of the transformed Meterpreter is as follows:
- During the data loading stage, use keep-alive long connections to maintain the transmission speed.
- During the sleep stage, use short connections to maintain concealment and can automatically recover when the network connection is interrupted (http short connection characteristics).
Specifically, the following code needs to be modified:
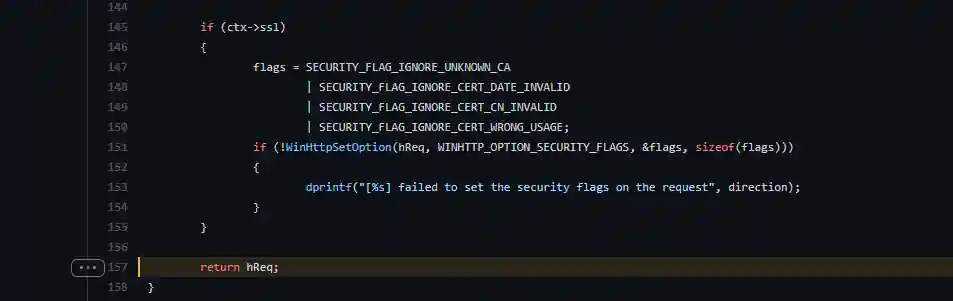
This function is used for http requests. The modified code is as follows:
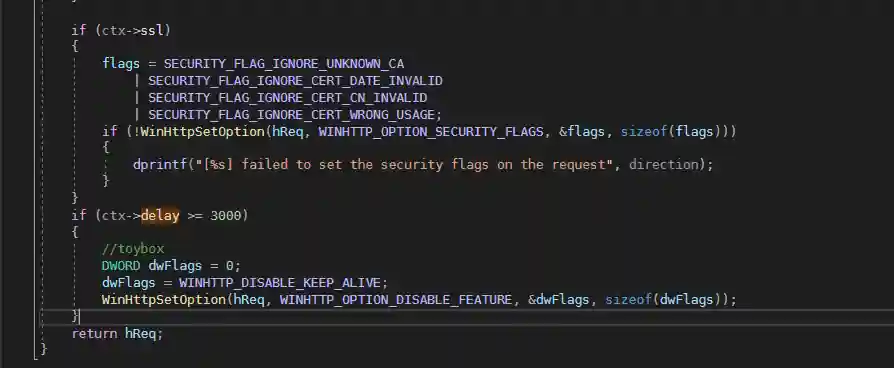
We add additional judgments in the code. If the heartbeat interval (delay) is greater than 3 seconds, the keep-alive function will be closed.
Heartbeat jitter feature
Cobalt Strike's heartbeat can add jitter function, that is, the sleep time is not a fixed value, but floats within a range. As a result, the time when Beacon requests the C2 is random, which can avoid detection to a certain extent.
Meterpreter may also support this feature by modifying the source code. The code is as follows:
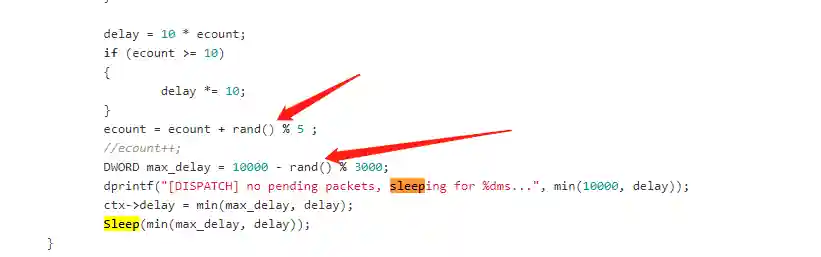
Among them, ecount is the heartbeat growth factor and max_delay is the maximum heartbeat interval. By adding random numbers to these two values, the heartbeat jitter function is implemented.
Engineering implementation
All code customization changes involved in the article have been merged into the following repository: